Space agencies raise risk of asteroid 2024 YR4 impacting Earth
The probability of a 2032 collision with the 50-meter asteroid has risen to 1.9%. However, ongoing calculations in the coming days and weeks may cause this estimate to fluctuate

The probability of asteroid 2024 YR4 colliding with Earth is increasing. The European Space Agency (ESA) now estimates a 1.8% chance of impact on January 22, 2032, while NASA has revised its calculations slightly higher to 1.9%. Despite these adjustments, there remains a more than 98% likelihood that the asteroid will pass by without posing any threat. Previously, the estimated probability of impact stood at 1.2%.
ESA’s Near-Earth Object Coordination Centre announced on Thursday that it will provide daily updates on the asteroid, which has now become the top-priority object of concern. These updates will incorporate observations from both ground-based and space-based telescopes. However, determining the exact trajectory of such a body is highly complex due to numerous influencing factors.
According to ESA, the asteroid has an estimated diameter of 40 to 90 meters and a current impact probability of around 1.5%. This classification “warrants the attention of astronomers” and has triggered intense observational efforts within the planetary defense community.

Asteroid 2024 YR4 is classified as a Level 3 object on the Turino Impact Hazard Scale, which ranks asteroid threats from 0 to 10. The ESA draws a comparison to Apophis, a 375-meter-wide space rock that briefly reached Level 4 in 2004. At its peak, Apophis had a 3% probability of impact, the highest ever recorded for an asteroid of significant size. However, further analysis of archival data from before 2004 confirmed that there was no risk of collision.
Discovered in December 2024 by the ATLAS Observatory in Chile, 2024 YR4 is too small to trigger a global catastrophe but could devastate a city if it were to strike a populated area. The severity of its impact would depend on several still-unknown factors, including its composition and entry angle into Earth’s atmosphere.
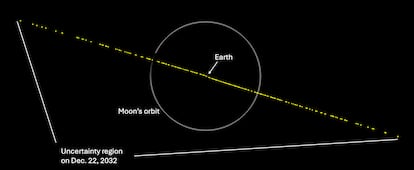
NASA’s Center for Near-Earth Object Studies (CNEOS) stated: ”In the unlikely event that 2024 YR4 is on an impact trajectory, the impact would occur somewhere along a risk corridor which extends across the eastern Pacific Ocean, northern South America, the Atlantic Ocean, Africa, the Arabian Sea, and South Asia.”
The agency has also released a graphic illustrating the current uncertainty in the asteroid’s trajectory, represented by a triangle. Only 1.6% of the area within this polygon corresponds to a potential impact with Earth.
Two specialized United Nations groups are currently studying the trajectory of asteroid 2024 YR4: the International Asteroid Warning Network (IAWN) and the Space Mission Planning Advisory Group (SMPAG). These organizations were established to coordinate the international response to potential asteroid threats. SMPAG, chaired by the ESA, brings together technical experts from major space agencies, including NASA. Its primary role is to recommend concrete actions for studying, mitigating, or deflecting hazardous asteroids if necessary.
On January 31, SMPAG held a virtual meeting to discuss the “the very small probability of an impact of asteroid 2024 YR4 in Dec 2032,” according to an official statement. The group is activated when an asteroid has a greater than 1% chance of impact and is larger than 50 meters. ”It was concluded that it is too early to take immediate action. However, SMPAG will monitor the evolution of impact threat and possible knowledge about the size closely,” the organization stated.
Asteroid 2024 YR4 follows a wide elliptical orbit around the Sun and is currently moving away from Earth in an almost straight line, making it difficult to study its curved trajectory. Over the next few months, the asteroid will begin to fade from view. To maximize data collection, during this period, ESA will coordinate observations of the asteroid with increasingly powerful telescopes, culminating in the use of the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile.
Asteroid 2024 YR4 may disappear from view before the possibility of a 2032 impact can be completely ruled out. If that happens, ESA has stated that the asteroid will likely remain on its risk list until it becomes observable again in 2028.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter to get more English-language news coverage from EL PAÍS USA Edition
Tu suscripción se está usando en otro dispositivo
¿Quieres añadir otro usuario a tu suscripción?
Si continúas leyendo en este dispositivo, no se podrá leer en el otro.
FlechaTu suscripción se está usando en otro dispositivo y solo puedes acceder a EL PAÍS desde un dispositivo a la vez.
Si quieres compartir tu cuenta, cambia tu suscripción a la modalidad Premium, así podrás añadir otro usuario. Cada uno accederá con su propia cuenta de email, lo que os permitirá personalizar vuestra experiencia en EL PAÍS.
¿Tienes una suscripción de empresa? Accede aquí para contratar más cuentas.
En el caso de no saber quién está usando tu cuenta, te recomendamos cambiar tu contraseña aquí.
Si decides continuar compartiendo tu cuenta, este mensaje se mostrará en tu dispositivo y en el de la otra persona que está usando tu cuenta de forma indefinida, afectando a tu experiencia de lectura. Puedes consultar aquí los términos y condiciones de la suscripción digital.