A beacon in the fight against HIV
In 20 years, the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief has saved 25 million lives and enabled 20 million people with HIV to start antiretroviral treatment, among other achievements. The director general of the WHO calls for it to continue
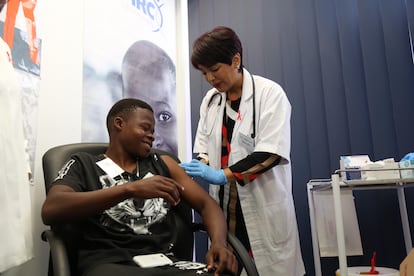
Twenty years ago, U.S. President George W. Bush, launched the U.S. President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief, or PEPFAR. When I came into office as Minister of Health of Ethiopia, I used funds from the program to save lives and reverse the HIV epidemic, which was sweeping across my country and much of the continent. U.S. leadership through PEPFAR helped to change the course of HIV in Africa.
Two decades on, and now as Director-General of the World Health Organization, I have seen the global impact of PEPFAR across the world, and particularly in Africa, Asia and Latin America. The stats are impressive: in twenty years the program has saved 25 million lives, enabled 20 million people with HIV to start antiretroviral treatment and prevented 5.5 million babies from being born with HIV. And five countries from sub-Saharan Africa — that were hit especially hard — are now reaching ambitious global targets of 95% of people living with HIV knowing their status, 95% of those diagnosed with the virus are receiving treatment and 95% of all those receiving lifesaving drugs will achieve viral suppression by 2025.
However, all these gains could now be in jeopardy.
The rising cost of living, new global conflicts and the climate crisis are all placing pressure on overseas development aid. This is squeezing the dollars for, and interest in, programs like PEPFAR that have had such broad impact on millions of people who are no longer condemned to ill health and early death because of where they were born.
As American representatives continue to debate reauthorizing PEPFAR for the next five years, it is worth reflecting on the legacy of this historic program for HIV and more broadly for global health.
In the 1980s, HIV was a death sentence for people who contracted it. However, by the mid-1990s, powerful new drug combinations had been developed that radically changed the course of the illness and global epidemic. Because of patent rules, these drugs were largely out-of-reach for people living in low- and middle-income countries, which ultimately meant millions of unnecessary deaths and 14 million orphans globally.
With media attention reflecting a global epidemic of death, the reduction of life-expectancy in Africa, threats to economies and health security, and with growing advocacy from people-powered movements, the American public called for action. And lawmakers on both sides of the aisle left politics behind and committed to one of the most ambitious health programs ever attempted.
Two decades later, PEPFAR’s track record of saving lives and stopping infections is something that people and politicians of all political colors can be proud of.
PEPFAR investment continues to be catalytic, driving a revolution not just in tackling HIV, but in how countries deliver health services. PEPFAR has not only provided the funds to purchase life-saving tests and treatments, but also invested in the systems and infrastructure required to ensure they reach people in need.
This approach has helped drive dramatic reductions not just in HIV infections but also deaths from malaria and tuberculosis, as well as steep drops in the number of mothers and their babies dying during childbirth.
WHO has worked with countries to take these achievements further and has certified 16 countries for the elimination of mother to child transmission of HIV. Other African countries are now stepping up and working hard to reach ambitious elimination targets.
Global progress against HIV is strong because of PEPFAR and its bilateral support to countries and ministries of health. Data has been used wisely and carefully to measure incidence, deaths and populations left behind. Mainstreaming that data into health programming has ensured that most resources are directed to the people at greatest risk, which is key to bending the curve of new infections.
The global impact of PEPFAR remains clearer than ever. Testing and treatment rates have increased; and 2022 saw the fewest new HIV infections in decades, with the largest declines in the countries and regions with the highest HIV burden.
But many people still start treatment too late and die with HIV, often without telling friends and family because of the stigma and discrimination they would face. New infections among children have not declined as fast as we hoped, and there are stark disparities in key at-risk communities. However, innovations to overcome some of these challenges, such as HIV self-testing, long-acting prevention and treatment options, are becoming more accessible and there is a renewed surge towards ending AIDS in children.
When President Bush started PEPFAR, the goal of an AIDS-free generation seemed completely implausible. Now it’s very real and feasible.
PEPFAR acted not only as a driver against a global public health threat, but it was also a sign of hope and solidarity from the American people to their brothers and sisters around the world. Today, leadership from the United States remains as critical as ever.
By reauthorizing PEPFAR, lawmakers would send a clear signal to the world that the United States remains committed to ending AIDS and to securing a healthy and safe world for all. Bridging the political divide changed the course of the AIDS global epidemic; keeping that bipartisan approach is our best bet toward one day being able to consign the disease to the history books.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter to get more English-language news coverage from EL PAÍS USA Edition
Tu suscripción se está usando en otro dispositivo
¿Quieres añadir otro usuario a tu suscripción?
Si continúas leyendo en este dispositivo, no se podrá leer en el otro.
FlechaTu suscripción se está usando en otro dispositivo y solo puedes acceder a EL PAÍS desde un dispositivo a la vez.
Si quieres compartir tu cuenta, cambia tu suscripción a la modalidad Premium, así podrás añadir otro usuario. Cada uno accederá con su propia cuenta de email, lo que os permitirá personalizar vuestra experiencia en EL PAÍS.
¿Tienes una suscripción de empresa? Accede aquí para contratar más cuentas.
En el caso de no saber quién está usando tu cuenta, te recomendamos cambiar tu contraseña aquí.
Si decides continuar compartiendo tu cuenta, este mensaje se mostrará en tu dispositivo y en el de la otra persona que está usando tu cuenta de forma indefinida, afectando a tu experiencia de lectura. Puedes consultar aquí los términos y condiciones de la suscripción digital.