From climate change to El Niño: Devastating power of Hurricane Otis surprises scientists
The natural disaster that devastated Acapulco strengthened from a tropical storm to a fearsome category 5 hurricane in just 12 hours
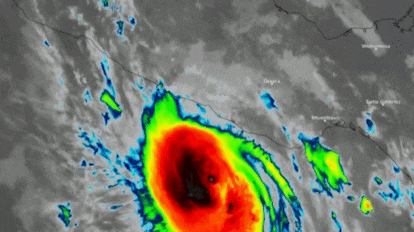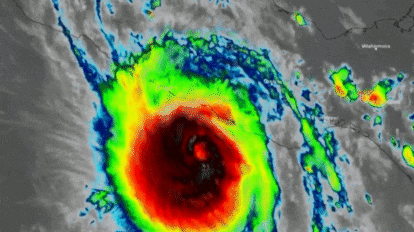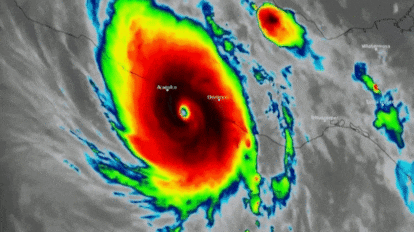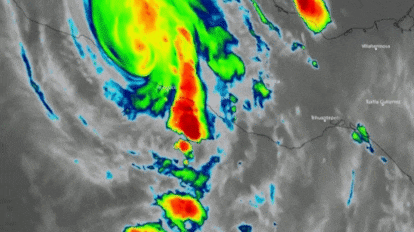
Hotels and homes destroyed, impassable roads and thousands of people cut off. This is how Acapulco, in the Mexican state of Guerrero, has been left after the passage of Hurricane Otis, the most powerful Pacific storm to make landfall on Mexican territory in the last 30 years. The cyclone, which in 12 hours went from a tropical storm to a category 5 hurricane, the highest possible classification, has left the popular tourist destination resembling a war zone with uprooted trees, debris, roofs torn off and buildings without walls. Neither the National Meteorological Service (SMN) nor local and federal authorities were able to predict the intensity of the hurricane. Scientists were also caught by surprise. The speed with which the cyclone intensified was unusual and forced Mexican authorities to issue an evacuation alert for the area just hours before Otis made landfall.
The SMN warned at 12:00 p.m. Tuesday, that the hurricane would reach Acapulco at 6:00 p.m. the following day. However, the storm arrived earlier than expected and devastated the coastal city at 12:25 a.m. Wednesday. Winds of more than 270 kilometers per hour (168 mph) hit the town and the state of Guerrero, one of the poorest in the country, destroying everything in their path. More than 500,000 people were left without electricity, internet and telephone connection in the early hours of the morning and only part of the service has so far been restored. The breakdown of communications has complicated access to the affected areas and there is still no official information on the number of victims and the amount of damage caused, although it is expected that material losses will amount to millions of dollars.

The unusual power of the hurricane has attracted the attention of the scientific community, which links the devastating power of Otis to the El Niño season, a phenomenon associated with changes in the atmosphere and the fluctuation of water temperature in the Pacific. “There is a hypothesis that it could be related to the rise in ocean temperature, which does not mean that there are more hurricanes, but it does mean that when there is one, the cyclone accelerates its formation by taking on more energy under these conditions,” explains Claudia Rojas of the Department of Process Engineering and Hydraulics of the Metropolitan Autonomous University (UAM).
There are those who point to a relationship between climate change and the strength of hurricanes, although the scientific community is still investigating the matter. “El Niño is inducing these cyclones to reach high categories. However, it is difficult to attribute the responsibility for Hurricane Otis to climate change,” says Christian Domínguez, a researcher at the Institute of Atmospheric Sciences of the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM). “What is known on a global scale is that with climate change there will be fewer hurricanes in the Pacific, but they will be more intense,” he adds. “With the information we currently have, it is not so clear that the intensity has to do with climate change because there are not so many historical records, although we have not ruled it out.”
After making landfall, Otis was downgraded to a tropical storm after depositing heavy rainfall in several states in central and southern Mexico. However, the threat has not yet passed. “The risk is not only posed by the strength of the winds. There are more dangers that such a phenomenon can entail, such as landslides and the flooding of rivers and streams,” says Domínguez. In Acapulco, some 20,000 people live in areas susceptible to flooding or landslides. The hurricane season in the Pacific begins around May 15 and ends around November 30, as such Guerrero could still experience the consequences of other cyclones, says Rojas. “Research work has shown that after a prolonged drought, very intense rainfall events occur, as is the case with tropical cyclones that can reach these [high] categories.”
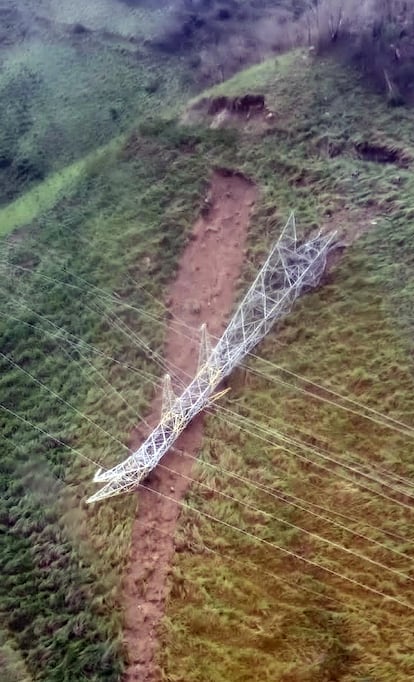

Otis is not the first hurricane in recent years to strengthen so rapidly. In 2015, Tropical Storm Patricia escalated to a Category 5 hurricane in 10 hours. The difference with the current phenomenon was that it did so offshore, and authorities in the states of Jalisco, Colima and Nayarit were able to evacuate 50,000 people before it made landfall. The storm, catalogued by the SMN as “extremely dangerous” and by the media as the “largest in history,” quickly lost strength after making landfall in Mexican territory thanks to the mountainous system of the Sierra Madre Occidental, which eroded the outer ring of the cyclone and prevented greater damage and devastation. Guerrero, in this case, did not have the same luck.
Acapulco International Airport, which receives millions of tourists every year, has been completely flooded and suffered serious damage to its infrastructure, forcing the suspension of all flights. The main highways are also closed, preventing communications with Mexico City. Mexican President Andrés Manuel López Obrador had ordered his Security Cabinet to go to the affected area, but on seeing the seriousness of the situation, he decided to personally supervise the rescue efforts himself. The Mexican army has initiated an emergency protocol and 37 shelters have been set up throughout the state for victims.

Sign up for our weekly newsletter to get more English-language news coverage from EL PAÍS USA Edition
Tu suscripción se está usando en otro dispositivo
¿Quieres añadir otro usuario a tu suscripción?
Si continúas leyendo en este dispositivo, no se podrá leer en el otro.
FlechaTu suscripción se está usando en otro dispositivo y solo puedes acceder a EL PAÍS desde un dispositivo a la vez.
Si quieres compartir tu cuenta, cambia tu suscripción a la modalidad Premium, así podrás añadir otro usuario. Cada uno accederá con su propia cuenta de email, lo que os permitirá personalizar vuestra experiencia en EL PAÍS.
¿Tienes una suscripción de empresa? Accede aquí para contratar más cuentas.
En el caso de no saber quién está usando tu cuenta, te recomendamos cambiar tu contraseña aquí.
Si decides continuar compartiendo tu cuenta, este mensaje se mostrará en tu dispositivo y en el de la otra persona que está usando tu cuenta de forma indefinida, afectando a tu experiencia de lectura. Puedes consultar aquí los términos y condiciones de la suscripción digital.